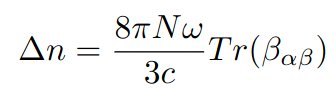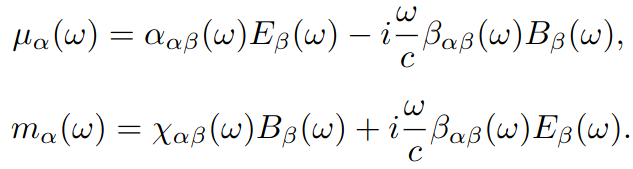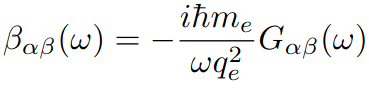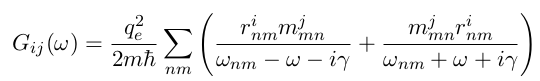Dichroism in molecules
Circular dichroism (CD) is dichroism involving circularly polarized light, i.e., the differential absorption of left- and right-handed light[1].
Dichroism in absorption can originate from an asymmetry in the dielectric tensor, which can be induced by the presence of either an external magnetic field or a spontaneous magnetization (MCD). This can be computed from the off-diagonal elements of the dielectric tensor. See the tutorial on The magneto-optical Kerr effect (MOKE). Another form of dichroism can be due to the chiral nature of molecules or materials[2] and goes under the name of natural circular dichroism (NCD). This latter can be related to the beta tensor and will be discussed in the present tutorial.
Few equations
NCD is described by the trace of the so called beta tensor
which related the electronic dipole to the time derivative of the applied magnetic field, and the magnetic dipole to the time derivative of the applied electric field
The latter can be obtained via the so called G tensor, which is similar to the dipole-dipole response function, but with electric and magnetic dipoles
The calculation of the magnetic dipoles is what makes NCD difficult to be computed in PBC, since these are not easily defined (solutions have been recently proposed in the literature). For isolated systems instead a simple sum over states can be employed (this is not possible in PBC because it involves diagonal intra-band dipoles):
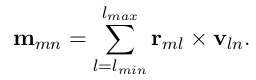
A detailed study of the convergence of the sum over states can be found in Ref.[3]. The same approach is also used in the Siesta code.
Prerequisites
Databases
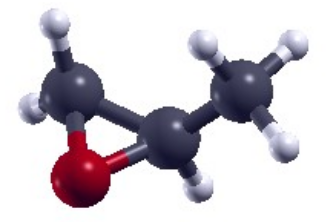
In this tutorial we will compute NCD on Propylene oxide, also known as R-Methyloxirane[4]. R-Methyloxirane has often been used in the literature as a benchmark molecule for NCD calculations against experimental data, due to its rigidity. To this end we provide a yambo database (DB) for R_methyloxirane.
- Yambo core databases (9 Mb): R_methyloxirane_DBs.tar.gz
Input files
To compute NCD a standard calculation of response function in transition space needs to be performed, also setting "dich" (short for dichroism) and eventually "trace" in the "BSE_prop" variable as below
BSEprop= "abs dich trace" # [BSS] abs/kerr/magn/dichr trace
Since the dipoles are obtained from a sum over states it is important to converge the number of states used in the equation, this can be controlled via the input variables
DipBandsALL # [DIP] Compute all bands range, not only valence and conduction DipApproach= "G-space v" # [DIP] [G-space v/R-space x/Covariant/Shifted grids] % DipBands 1 | 100 | # [DIP] Bands range for dipoles %
A standard input file for response function in transition space is (IP approximation)
optics # [R] Linear Response optical properties bse # [R][BSE] Bethe Salpeter Equation. dipoles # [R] Oscillator strenghts (or dipoles) BSEmod= "retarded" # [BSE] resonant/retarded/coupling BSKmod= "IP" # [BSE] IP/Hartree/HF/ALDA/SEX/BSfxc % BSEBands 1 | 20 | # [BSK] Bands range % % BEnRange 4.0000 | 7.00000 | eV # [BSS] Energy range % % BDmRange 0.10000 | 0.10000 | eV # [BSS] Damping range % BEnSteps= 1001 # [BSS] Energy steps % BLongDir 1.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | # [BSS] [cc] Electric Field %
A part from this, it is suggested to set the input variable which helps the convergence in isolated systems
rim_cut # [R] Coulomb potential NonPDirs= "XYZ" # [X/BSS] Non periodic chartesian directions (X,Y,Z,XY...) RandQpts=0 # [RIM] Number of random q-points in the BZ RandGvec= 1 RL # [RIM] Coulomb interaction RS components CUTGeo= "ws xyz" # [CUT] Coulomb Cutoff geometry: box/cylinder/sphere/ws X/Y/Z/XY.. % CUTBox 0.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | # [CUT] [au] Box sides % CUTRadius= 0.000000 # [CUT] [au] Sphere/Cylinder radius CUTCylLen= 0.000000 # [CUT] [au] Cylinder length CUTwsGvec= 0.700000 # [CUT] WS cutoff: number of G to be modified
Methyloxirane
CD at the Independent Particles approximation
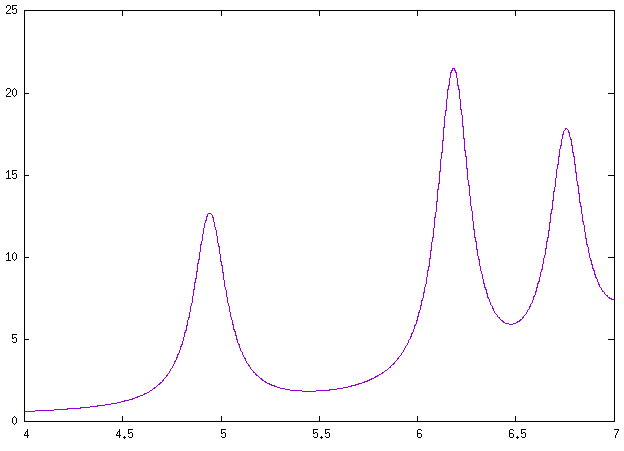
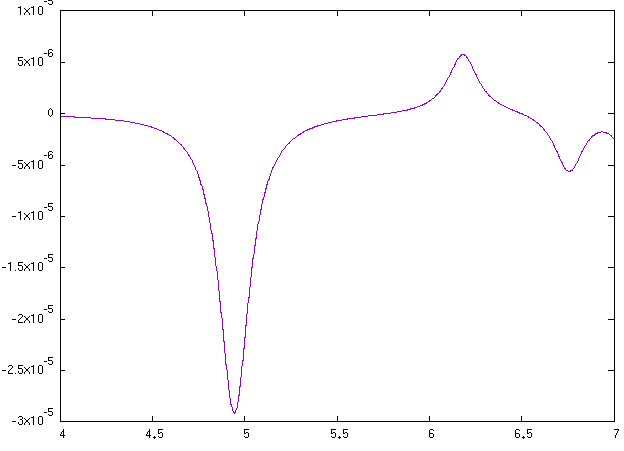
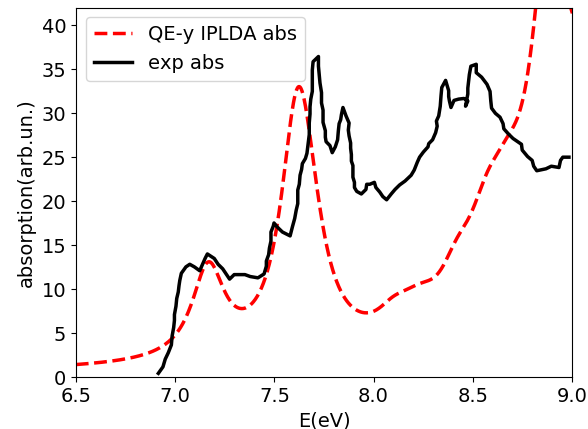
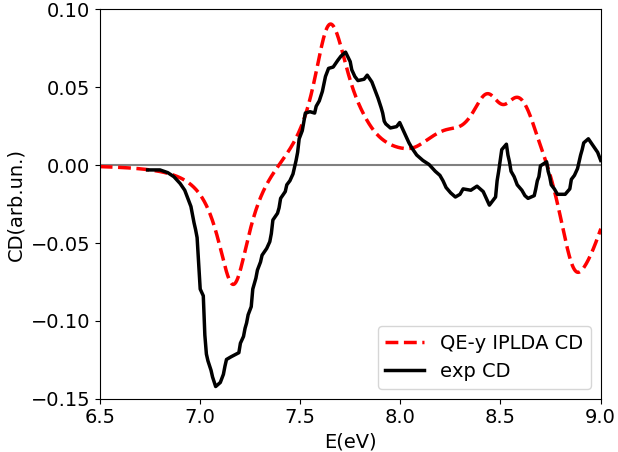
Here we use it to show how to compute NCD using the yambo code. Here we provide a poorly converged database, just to show how a calculation of NCD works with the yambo code. Using the input file provided above you will obtain the following plots for absorption (alpha file, on the left) and NCD (CD file, on the right):
Below we also report the results with converged parameters from [3]. This simulation was done with an FCC supercell of size 50 and an energy cutoff of 90 Ry, while for the tutorial we used a supercell of size 20 and an energy cutoff of 70 Ry in the QE run. Moreover a shift of X.XX eV was applied to align the spectra with the experimental data.
Beyond the Independent Particles approximation
References
- ↑ Circular Dichroism on wikipedia
- ↑ Chiral Media on wikipedia
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 E. Molteni, G. Cappellini, and D. Sangalli, Ab initio circular dichroism with the Yambo code: applications to dipeptides, IOP Conf. Series: Materials Science and Engineering 1265, 012005 (2022)
- ↑ Propylene oxide on wikipedia