Calculating optical spectra including excitonic effects: a step-by-step guide
This tutorial guides you through the workflow of a calculation of the optical spectrum of a given material by solving the Bethe-Salpeter equation. Specifically, we will use bulk h-BN as an example.
Before starting, you need to obtain the tarballs for hBN. See instructions on the main tutorials page.
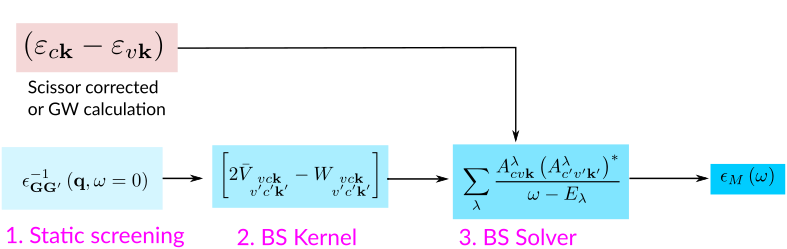
The target quantity in a Bethe-Salpeter calculation is the macroscopic dielectric matrix εM. The following quantities/steps are needed to obtain εM:
The optical absorption spectrum corresponds to ImεM(ω). Following this scheme we go through the flow of a calculation:
Step 1: Static screening
Use the SAVE folders that are already provided and type:
$ cd YAMBO_TUTORIALS/hBN/YAMBO
Follow the Static screening module and then return to this tutorial
Step 2: Bethe-Salpeter kernel
Follow the module on Bethe-Salpeter kernel and return to this tutorial
Step 3: Diagonalisation of the excitonic Hamiltonian
This is the step in which you obtain the spectra. Mathematically this implies solving a large eigenvalue problem. In this tutorial, we diagonalise the whole Bethe-Salpeter matrix, but there are other numerical approaches available in Yambo. The difference between these approaches and when they should be used is the object of one of the next tutorials.
Follow the module on Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization then return to this tutorial
Step 4: Include previous quasiparticle (GW) results
In Step 3, we included the quasiparticle corrections to the Kohn-sham energies as a scissor operator. An alternative is to use the results from a previous run of Yambo.
Follow the module on Bethe-Salpeter on top of quasiparticle energies and return to this tutorial
Links
- Back to Modena 2025
- Back to Rome 2023#Tutorials
- Back to technical modules menu
- Back to tutorials menu