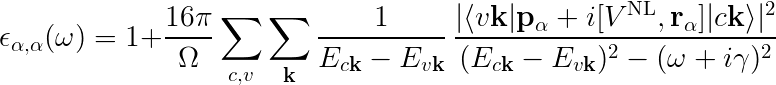Optics at the independent particle level
In this tutorial you will learn how to calculate optical spectra at the RPA or independent particle level for bulk hBN.
Prerequisites
- You must first complete the "How to use Yambo" tutorial
You will need:
- The
SAVEdatabases for bulk hBN - The
yamboexecutable gnuplot, for plotting spectra
Choosing input parameters
Enter the folder for bulk hBN that contains the SAVE directory, and generate the input file. From yambo -H you should understand that the correct option is yambo -o c. Let's add some command line options:
$ cd YAMBO_TUTORIALS/hBN/YAMBO $ yambo -o c -F yambo.in_IP -J Full
This corresponds to optical properties in G-space at the independent particle level (Chimod= "IP").
Let's calculate just for the long-wavelength limit q = 0. This always corresponds to the first q-point. Changing the appropriate variable range in the input file to:
% QpntsRXd 1 | 1 | # [Xd] Transferred momenta %
Save the input file and launch the code, keeping the command line options as before (i.e., just remove the lower case options):
$ yambo -F yambo.in_IP -J Full ... <---> [05] Optics <---> [LA] SERIAL linear algebra <---> [DIP] Checking dipoles header <---> [x,Vnl] computed using 4 projectors <---> [M 0.017 Gb] Alloc WF ( 0.016) <---> [WF] Performing Wave-Functions I/O from ./SAVE <01s> Dipoles: P and iR (T): |########################################| [100%] 01s(E) 01s(X) <01s> [M 0.001 Gb] Free WF ( 0.016) <01s> [DIP] Writing dipoles header <01s> [X-CG] R(p) Tot o/o(of R) : 5501 52992 100 <01s> Xo@q[1] |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X) <01s> [06] Game Over & Game summary $ ls Full SAVE yambo.in_IP r_setup o-Full.eel_q1_ip o-Full.eps_q1_ip r-Full_optics_chi
Let's take a moment to understand what Yambo has done in side the Optics runlevel:
- Compute the [x,Vnl] term
- Read the wavefunctions from disc [WF]
- Compute the dipoles, i.e. matrix elements of p
- Write the dipoles to disk as
SAVE/ndb.dip*databases. This you can see in the report file:
$ grep -A20 "WR" r-Full_optics_chi [WR./Full//ndb.dip_iR_and_P] Brillouin Zone Q/K grids (IBZ/BZ): 14 72 14 72 RL vectors (WF): 1491 Electronic Temperature [K]: 0.0000000 Bosonic Temperature [K]: 0.0000000 X band range : 1 100 RL vectors in the sum : 1491 [r,Vnl] included :yes ...
- Finally, Yambo computes X0 for this q, and generates
o-Full.eps_q1_ipfile for plotting