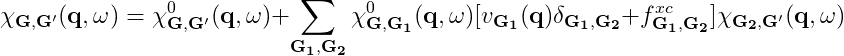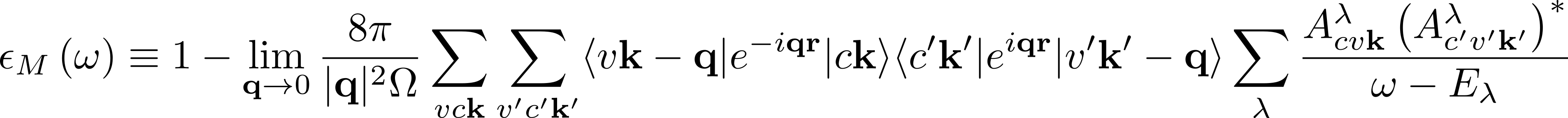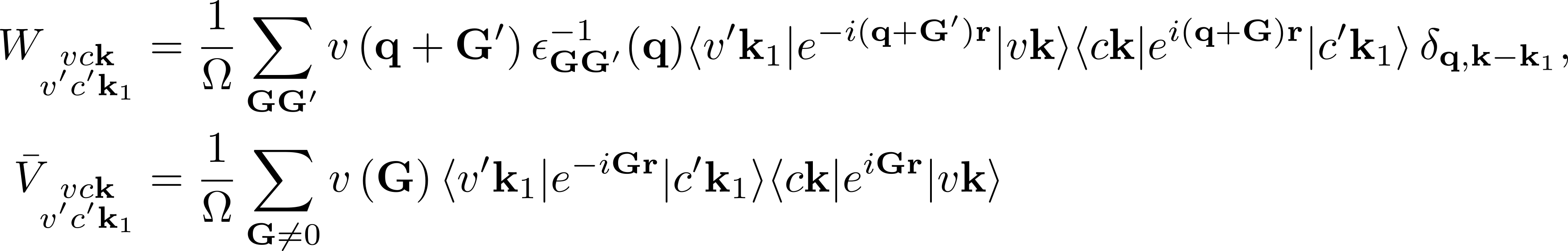How to choose the input parameters: Difference between revisions
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
'''ADD COMMAND''' | '''ADD COMMAND''' | ||
For the purpose of this exercise we will use: | |||
[[Variables#NGsBlkXs|NGsBlkXs]] = 4 Ry | |||
%[[Variables#BndsRnXs|BndsRnXs]] | |||
1 | 40 | | |||
% | |||
==Convergence of the macroscopic dielectric function== | ==Convergence of the macroscopic dielectric function== | ||
Revision as of 21:51, 17 April 2017
In the previous tutorial, you have been guided step-by-step through the calculations of the optical spectrum of bulk hBN by solving the Bethe-Salpeter equation. The values for the relevant input parameters have then been given to you.
In this tutorial you will learn how to choose those parameters. These parameters are related either to the truncation of infinite sums or to the approximations of infinitesimal with small, but finite quantities. A wrong choice of these parameters can lead to inaccurate or even physically wrong results. One then needs to run a series of calculations by changing the parameters till the results are converged , meaning they are changing by a negligible amount.
Note that all the following operations can be automated. A useful python-based interface to yambo, yambopy, can be used for this purpose. It is worth however to go at least once through the pain of a 'by-hand' convergence study so to better understand the automated process for few of those variables.
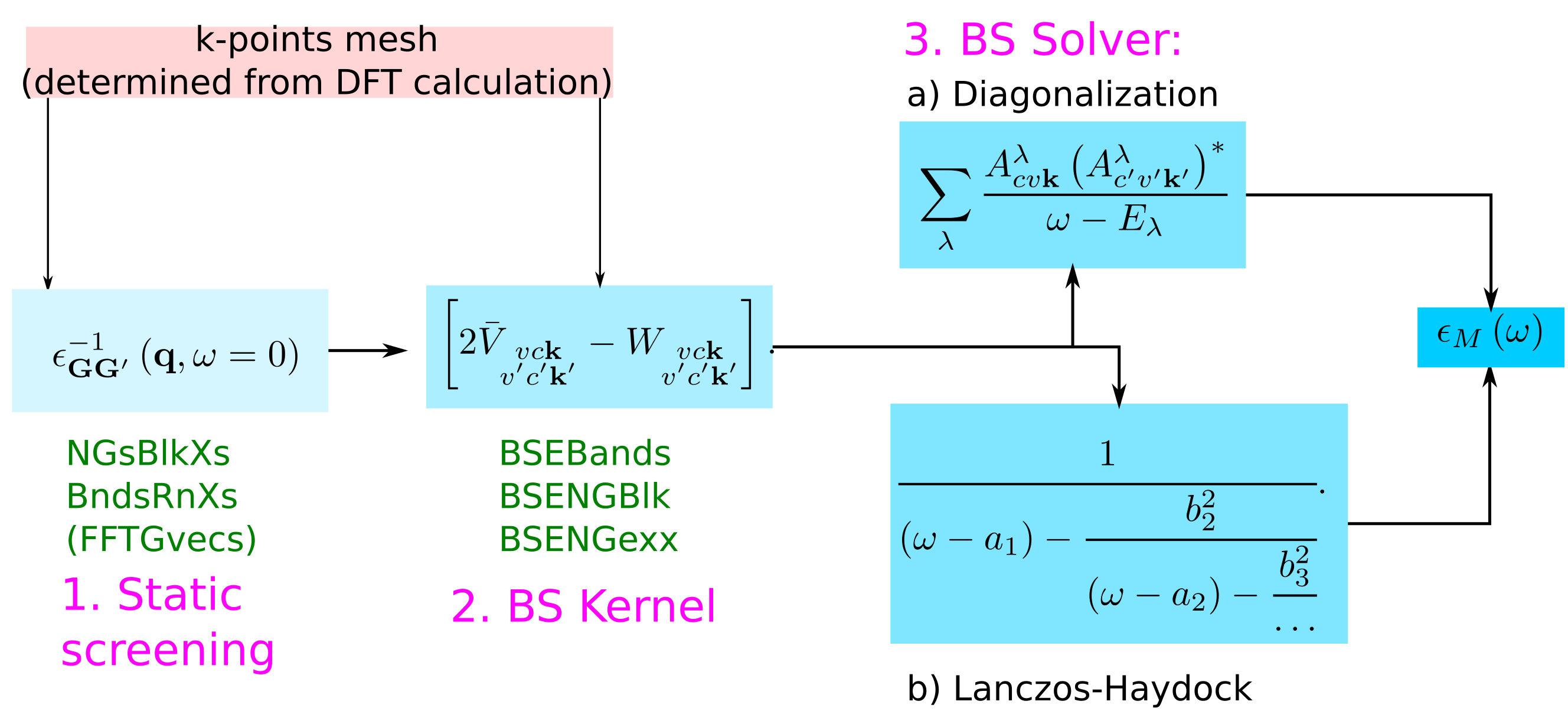
Coming back to the scheme to calculate the macroscopic dielectric matrix within Bethe-Salpeter, here the list of the parameters that have to be determined by convergence studies:
Though we will discuss those parameters, we will run examples only for the BS kernel part.
Convergence of the static screening
The parameters that need to be converged can be understood by looking at the equations:
where χGG' is given by
NGsBlkXs: The dimension of the microscopic inverse matrix, related to Local fieldsBndsRnXs: The sum on bands in the independent particle χ0GG'
Furthermore as shown in this tutorial one can reduce the value of
since generally, fewer G-vectors are needed than what are needed in DFT calculations. This can be critical for large calculations, or for supercells with a lot of vacuum.
Note that this parameter appear only when the input is generated specifying the verbosity level -V RL
The convergence for the static screening then is similar to the convergence of other response functions and the plasmon pole in GW calculations and won't be covered here. Note in fact that you can re-use the database obtained (and converged) from a previous plasmon pole calculation as long as the same k-points are used
ADD COMMAND
For the purpose of this exercise we will use:
NGsBlkXs = 4 Ry %BndsRnXs 1 | 40 | %
Convergence of the macroscopic dielectric function
In the expression for the macroscopic dielectric function
depends on the summation over the pair of quasiparticle states vck.
BSEBands: defines the vc pairs.- the k-point mesh of the DFT calculations defines the k
Basically we need a large enough basis of transitions (pair of quasiparticle states) to correctly describe the excitons in the energy region of interest.
Furthermore, in the kernel part
summations over G vectors appear:
BSENGblk: defines the screened interaction block size (double sum in W).BSENGexx: defines the components of Hartree potential (the sum in V).
In the following we will see how the spectrum depends on these parameters.