Bulk material: h-BN: Difference between revisions
(→Files) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
* Plane wave cutoff 40 Ry (1500 RL vectors in wavefunctions) | * Plane wave cutoff 40 Ry (1500 RL vectors in wavefunctions) | ||
== | == DFT calculations == | ||
Unpack the | Unpack the tarfile. It uses the same file structure as other yambo tutorials: | ||
$ tar -xcvf hBN-bulk.tar | $ tar -xcvf hBN-bulk.tar | ||
$ cd YAMBO_TUTORIALS/hBN/PWSCF | $ cd YAMBO_TUTORIALS/hBN/PWSCF | ||
| Line 22: | Line 22: | ||
hbn_bands.in hbn_nscf.in hbn_scf.in hbn_scf_b.in REFERENCES | hbn_bands.in hbn_nscf.in hbn_scf.in hbn_scf_b.in REFERENCES | ||
First run the SCF calculation to generate the ground-state charge density, occupations, Fermi level, and so on: | |||
First run the SCF calculation | |||
pw.x < hBN_scf.in > hBN_scf.out | pw.x < hBN_scf.in > hBN_scf.out | ||
Next run a non-SCF calculation to generate a set of Kohn-Sham eigenvalues and eigenvectors across a denser k-point mesh, for occupied and unoccupied states: | |||
pw.x < hBN_nscf.in > hBN_nscf.out | pw.x < hBN_nscf.in > hBN_nscf.out | ||
Note the presence of the following flags in the input file: | Note the presence of the following flags in the input file: | ||
Revision as of 15:49, 22 March 2017
In this tutorial you will learn how to generate the Yambo SAVE folder for bulk hBN starting from a PWscf calculation.
Prerequisites
You will need:
- PWSCF input files and pseudopotentials for hBN bulk (Download here)
pw.xexecutable, version 5.0 or laterp2yexecutable
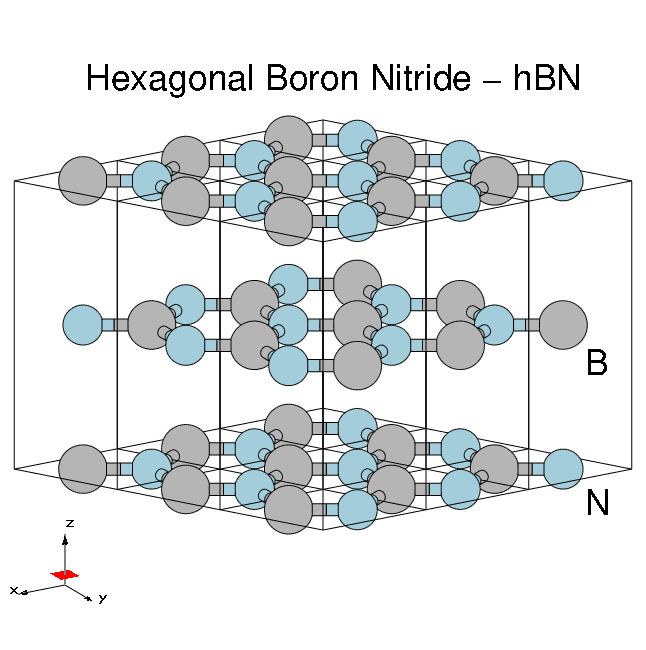
Material properties
Hexagonal boron nitride - hBN:
- HCP lattice, ABAB stacking
- Four atoms per cell, B and N (16 electrons)
- Lattice constants: a = 4.716 [a.u.], c/a = 2.582
- Plane wave cutoff 40 Ry (1500 RL vectors in wavefunctions)
DFT calculations
Unpack the tarfile. It uses the same file structure as other yambo tutorials:
$ tar -xcvf hBN-bulk.tar $ cd YAMBO_TUTORIALS/hBN/PWSCF $ ls hbn_bands.in hbn_nscf.in hbn_scf.in hbn_scf_b.in REFERENCES
First run the SCF calculation to generate the ground-state charge density, occupations, Fermi level, and so on:
pw.x < hBN_scf.in > hBN_scf.out
Next run a non-SCF calculation to generate a set of Kohn-Sham eigenvalues and eigenvectors across a denser k-point mesh, for occupied and unoccupied states:
pw.x < hBN_nscf.in > hBN_nscf.out
Note the presence of the following flags in the input file:
wf_collect=.true. force_symmorphic=.true.
which are needed for the next step. Full explanations of these variables are given on the quantum-ESPRESSO input variables page. After these two runs, you should have a hBN.save directory:
$ ls hBN.save data-file.xml
Conversion to Yambo format
PWscf output is converted to the Yambo format using the p2y (pwscf to yambo), found in the yambo bin directory.
Enter the hbn.save directory and launch p2y:
$ cd hBN.save $ p2y [output]
The code reports some information about the system and generates a SAVE directory:
$ ls SAVE HB,in etc $ ls SAVE ns.db1 ns.wf ns.kb_pp_pwscf ns.wf_fragments_1_1 ... ns.kb_pp_pwscf_fragment_1 ...
Finally, let's move the SAVE directory into a new clean folder:
mv SAVE ../YAMBO/
Advanced users
p2y accepts several command line options:
$ p2y -H
dfadsfas