Optical properties at finite temperature: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In this tutorial we will show you how to calculate optical properties including thermal effects due to the electron-phonon coupling. | |||
This tutorial assumes that you have completed all the steps from the previous tutorial on [[Electron Phonon Coupling]]. | |||
== Absorption at finite temperature == | == Absorption at finite temperature == | ||
Now you repeat the previous calculation but including all k-points, the last 3 valence and the first 3 conduction bands: | Now you repeat the previous calculation but including all k-points, the last 3 valence and the first 3 conduction bands: | ||
| Line 42: | Line 41: | ||
The same procedure can be applied to the Bethe-Salpeter calculations. However in this case results can be slightly wrong. If fact electron-phonon matrix elements should be rotate in the excitonic space, as it was done in ref. <ref> see Supp. Mat. of [https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.99.081109 Phys. Rev. B '''99''', 081109(R) (2019)]</ref><ref>F. Paleari, [https://orbilu.uni.lu/handle/10993/41058 Phd Thesis (2019)]</ref>, while at present Yambo calculate the exciton width from the correction to the single particle bands, see ref. <ref name=marini>A. Marini, [https://arxiv.org/abs/0712.3365 Phys. Rev. Lett. '''101''' 106405 (2008)]</ref> . This approximation is correct in case of not-strong bounded excitons, and unfortunately this is not the case. | The same procedure can be applied to the Bethe-Salpeter calculations. However in this case results can be slightly wrong. If fact electron-phonon matrix elements should be rotate in the excitonic space, as it was done in ref. <ref> see Supp. Mat. of [https://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.99.081109 Phys. Rev. B '''99''', 081109(R) (2019)]</ref><ref>F. Paleari, [https://orbilu.uni.lu/handle/10993/41058 Phd Thesis (2019)]</ref>, while at present Yambo calculate the exciton width from the correction to the single particle bands, see ref. <ref name=marini>A. Marini, [https://arxiv.org/abs/0712.3365 Phys. Rev. Lett. '''101''' 106405 (2008)]</ref> . This approximation is correct in case of not-strong bounded excitons, and unfortunately this is not the case. | ||
== Excitonic Eliashberg Functions == | |||
== Phonon-assisted density of states == | |||
Revision as of 08:32, 25 February 2021
In this tutorial we will show you how to calculate optical properties including thermal effects due to the electron-phonon coupling. This tutorial assumes that you have completed all the steps from the previous tutorial on Electron Phonon Coupling.
Absorption at finite temperature
Now you repeat the previous calculation but including all k-points, the last 3 valence and the first 3 conduction bands:
..... %QPkrange # [GW] QP generalized Kpoint/Band indices 1|8|2|7| % ....
and save the results of the 0K and 300K temperature in two separate folder with the -J option. Now you can use the correction to the energy levels and the induced width to calculate the optical absorption at finite temperature. Generate the input with the command yambo_ph -o c -V qp
optics # [R] Linear Response optical properties
chi # [R][CHI] Dyson equation for Chi.
dipoles # [R] Oscillator strenghts (or dipoles)
Chimod= "IP" # [X] IP/Hartree/ALDA/LRC/PF/BSfxc
% QpntsRXd
1 | 1 | # [Xd] Transferred momenta
%
% BndsRnXd
2 | 7 | # [Xd] Polarization function bands
%
% EnRngeXd
0.000000 | 5.000000 | eV # [Xd] Energy range
%
% DmRngeXd
0.0100000 | 0.0100000 | eV # [Xd] Damping range
%
ETStpsXd= 500 # [Xd] Total Energy steps
% LongDrXd
1.000000 | 0.000000 | 0.000000 | # [Xd] [cc] Electric Field
%
XfnQPdb= "E W < T300/ndb.QP" # [EXTQP Xd] Database action
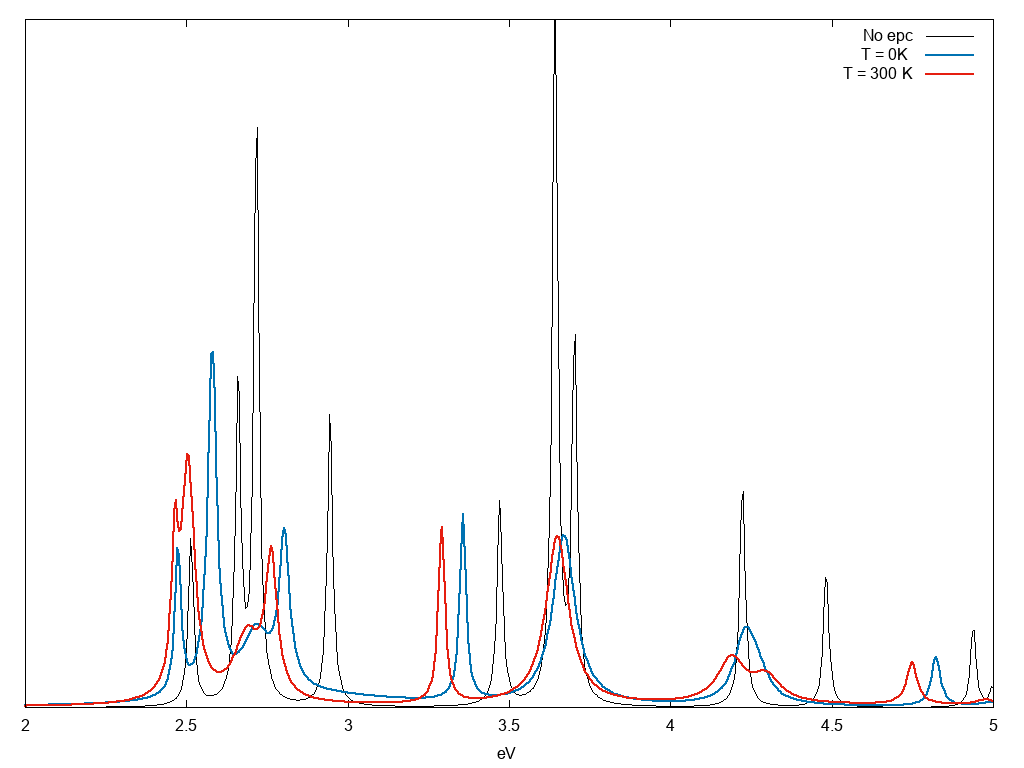
set the path of the ndb.QP you want to read and perform the calculations. Notice that from the QP database we read two quantities the correction to the energy levels E and the width W. In this calculation we also included a small smearing 0.01eV to mimic the electronic smearing. Hereafter the result without and with electron-phonon coupling at two different temperatures:
The same procedure can be applied to the Bethe-Salpeter calculations. However in this case results can be slightly wrong. If fact electron-phonon matrix elements should be rotate in the excitonic space, as it was done in ref. [1][2], while at present Yambo calculate the exciton width from the correction to the single particle bands, see ref. [3] . This approximation is correct in case of not-strong bounded excitons, and unfortunately this is not the case.
Excitonic Eliashberg Functions
Phonon-assisted density of states
- ↑ see Supp. Mat. of Phys. Rev. B 99, 081109(R) (2019)
- ↑ F. Paleari, Phd Thesis (2019)
- ↑ A. Marini, Phys. Rev. Lett. 101 106405 (2008)