Bulk material: h-BN: Difference between revisions
m (Still playing with Navigation) |
m (Still playing with Navigation) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{| style="width:100%" border="1" | {| style="width:100%" border="1" | ||
|style="width:33%; text-align:left"|Prev: | |style="width:33%; text-align:left"|Prev: [[First_steps:_a_walk_through_from_DFT_to_optical_properties|First steps]] | ||
|style="width:33%; text-align:center"| | |style="width:33%; text-align:center"|Address: [[Tutorials]] -> [[First_steps:_a_walk_through_from_DFT_to_optical_properties|First steps]] -> [[Bulk_material:_h-BN|bulk hBN]] | ||
|style="width:33%; text-align:right"|Next: [[2D_material:_h-BN_sheet|2D hBN]] | |style="width:33%; text-align:right"|Next: [[2D_material:_h-BN_sheet|2D hBN]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 104: | Line 103: | ||
* How to check the contents of the netCDF databases | * How to check the contents of the netCDF databases | ||
{| style="width:100%" border="1" | {| style="width:100%" border="1" | ||
|style="width:33%; text-align:left"|Prev: | |style="width:33%; text-align:left"|Prev: [[First_steps:_a_walk_through_from_DFT_to_optical_properties|First steps]] | ||
|style="width:33%; text-align:center"| | |style="width:33%; text-align:center"|Address: [[Tutorials]] -> [[First_steps:_a_walk_through_from_DFT_to_optical_properties|First steps]] -> [[Bulk_material:_h-BN|bulk hBN]] | ||
|style="width:33%; text-align:right"|Next: [[2D_material:_h-BN_sheet|2D hBN]] | |style="width:33%; text-align:right"|Next: [[2D_material:_h-BN_sheet|2D hBN]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 12:35, 20 April 2017
| Prev: First steps | Address: Tutorials -> First steps -> bulk hBN | Next: 2D hBN |
In this module you will learn how to generate the Yambo SAVE folder for bulk hBN starting from a PWscf calculation.
Prerequisites
You will need:
- PWSCF input files and pseudopotentials for hBN bulk
pw.xexecutable, version 5.0 or laterp2yandyamboexecutables
System characteristics
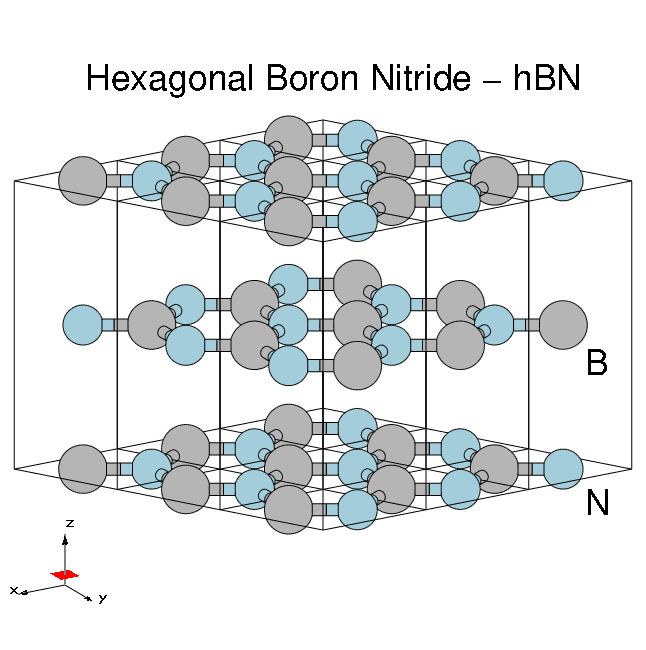
Hexagonal boron nitride - hBN:
- HCP lattice, ABAB stacking
- Four atoms per cell, B and N (16 electrons)
- Lattice constants: a = 4.716 [a.u.], c/a = 2.582
- Plane wave cutoff 40 Ry (~1500 RL vectors in wavefunctions)
- SCF run: shifted 6x6x2 grid (12 k-points) with 8 bands
- Non-SCF run: gamma-centred 6x6x2 (14 k-points) grid with 100 bands
DFT calculations
$ cd YAMBO_TUTORIALS/hBN/PWSCF $ ls Inputs Pseudos PostProcessing References hBN_scf.in hBN_nscf.in hBN_scf_plot_bands.in hBN_nscf_plot_bands.in
First run the SCF calculation to generate the ground-state charge density, occupations, Fermi level, and so on:
$ pw.x < hBN_scf.in > hBN_scf.out
Inspection of the output shows that the valence band maximum lies at 5.06eV.
Next run a non-SCF calculation to generate a set of Kohn-Sham eigenvalues and eigenvectors for both occupied and unoccupied states (100 bands):
$ pw.x < hBN_nscf.in > hBN_nscf.out
Here we use a 6x6x2 grid giving 14 k-points, but denser grids should be used for checking convergence of Yambo runs.
Note the presence of the following flags in the input file:
wf_collect=.true. force_symmorphic=.true. diago_thr_init=5.0e-6, diago_full_acc=.true.
which are needed for generating the Yambo databases accurately. Full explanations of these variables are given on the quantum-ESPRESSO input variables page.
After these two runs, you should have a hBN.save directory:
$ ls hBN.save data-file.xml charge-density.dat gvectors.dat B.pz-vbc.UPF N.pz-vbc.UPF K00001 K00002 .... K00035 K00036
Conversion to Yambo format
The PWscf bBN.save output is converted to the Yambo format using the p2y executable (pwscf to yambo), found in the yambo bin directory.
Enter hBN.save and launch p2y:
$ cd hBN.save $ p2y ... <---> DBs path set to . <---> Index file set to data-file.xml <---> Header/K-points/Energies... done ... <---> == DB1 (Gvecs and more) ... <---> ... Database done <---> == DB2 (wavefunctions) ... done == <---> == DB3 (PseudoPotential) ... done == <---> == P2Y completed ==
This output repeats some information about the system and generates a SAVE directory:
$ ls SAVE ns.db1 ns.wf ns.kb_pp_pwscf ns.wf_fragments_1_1 ... ns.kb_pp_pwscf_fragment_1 ...
These files, with an n prefix, indicate that they are in netCDF format, and thus not human readable. However, they are perfectly transferable across different architectures. You can check that the databases contain the information you expect by launching Yambo using the -D option:
$ yambo -D [RD./SAVE//ns.db1]------------------------------------------ Bands : 100 K-points : 14 G-vectors [RL space]: 8029 Components [wavefunctions]: 1016 ... [RD./SAVE//ns.wf]------------------------------------------- Fragmentation :yes ... [RD./SAVE//ns.kb_pp_pwscf]---------------------------------- Fragmentation :yes - S/N 006626 -------------------------- v.04.01.02 r.00000 -
In practice we suggest to move the SAVE folder into a new clean folder.
In this tutorial however, we ask instead that you continue using a SAVE folder that we prepared previously:
$ cd ../../YAMBO $ ls SAVE
Summary
From this tutorial you've learned:
- How to run a DFT calculation with PWscf in preparation for Yambo
- Convert the DFT output into the Yambo format
- How to check the contents of the netCDF databases
| Prev: First steps | Address: Tutorials -> First steps -> bulk hBN | Next: 2D hBN |