Bethe-Salpeter on top of quasiparticle energies: Difference between revisions
| (23 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In this module you will learn how to include GW-corrected (QP) energies in the calculation of the absorption spectrum. | In this module, you will learn how to include GW-corrected (QP) energies in the calculation of the absorption spectrum. The energy differences on the diagonal of the excitonic Hamiltonian are added before the solution of the Bethe-Salpeter eigenproblem, therefore only that step needs to be repeated if we change the QP corrections. | ||
== Prerequisites == | |||
'''Previous modules''' | |||
You must have completed | |||
* the [[Bethe-Salpeter kernel|BSE kernel]] tutorial | |||
* the [[Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization| Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization]] tutorial, in which a simple scissor operator is used for the QP corrections. | |||
'''You will need''': | |||
* The <code>SAVE</code> databases for 3D hBN | |||
* The <code>3D_BSE</code> directory containing the databases from the [[Static screening]], [[Bethe-Salpeter kernel]], [[Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization]] modules thus containing the <code>ndb.BS_Q1_CPU_0</code> and <code>ndb.em1s*</code> databases for 3D hBN | |||
* The <code>GW_QP_database</code> directory (provided) which contains the database with the GW corrections (you can also use the ndb.QP file produced in the GW tutorial) | |||
* <code>yambo </code> executable | |||
''' | |||
==Reading the QP corrections from a previous ''GW'' calculation== | ==Reading the QP corrections from a previous ''GW'' calculation== | ||
In [[Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization| | In [[Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization|the previous step]] we used a simple scissor operator to correct the Kohn-Sham DFT energies. Instead, in this part, we are taking the QP corrections from a previous Yambo GW calculation. | ||
We create and edit the input: | We create and edit the input: | ||
$yambo -F 03_3D_QP_BSE.in -y d -V qp -J 3D_BSE | $ yambo -F 03_3D_QP_BSE.in -y d -V qp -J 3D_BSE | ||
We set all parameters as in the previous | We set all parameters as in [[Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization| the previous step]], except for the part regarding the QP correction: | ||
[[Variables#KfnQPdb|KfnQPdb]]= "E < | [[Variables#KfnQPdb|KfnQPdb]]= "E < GW_QP_database/ndb.QP" # [EXTQP BSK BSS] Database | ||
[[Variables#KfnQP_N| | [[Variables#KfnQP_N|KfnQP_INTERP_NN]]= 1 # [EXTQP BSK BSS] Interpolation neighbours | ||
% [[Variables#KfnQP_E|KfnQP_E]] | % [[Variables#KfnQP_E|KfnQP_E]] | ||
0.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | # [EXTQP BSK BSS] E parameters (c/v) eV|adim|adim | 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | # [EXTQP BSK BSS] E parameters (c/v) eV|adim|adim | ||
% | % | ||
Instead of setting the values for the scissor, we give the path to | Instead of setting the values for the scissor, we give the path to the database that contains the QP corrections (<code>GW_QP_database/ndb.QP</code>). The latter was created by running a GW calculation as in [[GW hBN Yambo Virtual 2021 version#Step 3: Interpolating Band Structures|Step 3]] of the GW tutorial. For more info about how the QP corrections are loaded you can also check this page: [[Loading QP corrections]]. <br> | ||
Run Yambo: | Run Yambo: | ||
$ yambo -F 03_3D_QP_BSE.in -J "3D_QP_BSE,3D_BSE" | $ yambo -F 03_3D_QP_BSE.in -J "3D_QP_BSE,3D_BSE" | ||
Note how we specified multiple directories, separated by a comma. This instructs Yambo to look for databases that may be already present from previous steps of the calculations in all the listed folders. If you completed the [[Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization|previous section]] of the tutorial, then you should have the <code>3D_BSE</code> folder with <code>ndb.dipoles_*</code>, <code>ndb.em1s*</code> and <code>ndb.BS_CPU*</code> databases, which will not be recalculated by Yambo: the code will repeat only the diagonalization step - also reading the QP database - and print the resulting databases in the new folder <code>3D_QP_BSE</code>. If you don't have the <code>3D_BSE</code> folder, you have to repeat the entire BSE calculation, therefore you just need to give the option "-J 3D_QP_BSE,GW_QP_database". | |||
This produces the following log in the standard output. Note Section 4 (regarding external QP corrections to the kernel): | This produces the following log in the standard output. Note Section 4 (regarding external QP corrections to the kernel): | ||
<---> [04] External/Internal QP corrections | <---> [04] External/Internal QP corrections | ||
<---> E< | <---> E<GW_QP_database/ndb.QP[ PPA@E 27.21138 = XG 5 = Xb 1-40 = Scb 1-40] | ||
<---> [dE_from_DB-Nearest K] Exact matches : 100.0000 [o/o] | <---> [dE_from_DB-Nearest K] Exact matches : 100.0000 [o/o] | ||
This tells you that the file was found, read correctly and that the '''k''' points found in the file matched the ones you are using for the current calculation (otherwise interpolation would be needed). | This tells you that the file was found, read correctly and that the '''k''' points found in the file matched the ones you are using for the current calculation (otherwise interpolation would be needed). | ||
It is crucial to check that the file has been read, since if not Yambo gives a warning but continues the calculation (with no QP corrections at all!). | It is crucial to check that the file has been read, since if not Yambo gives a warning but continues the calculation (with no QP corrections at all!). | ||
As in the | As in the calculation with the scissor shift the final results are the files with the macroscopic dielectric functions. Let's compare the results for the optical absorption spectrum with those obtained [[Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization|previously]] with a simple scissor: | ||
$ gnuplot | $ gnuplot | ||
... | ... | ||
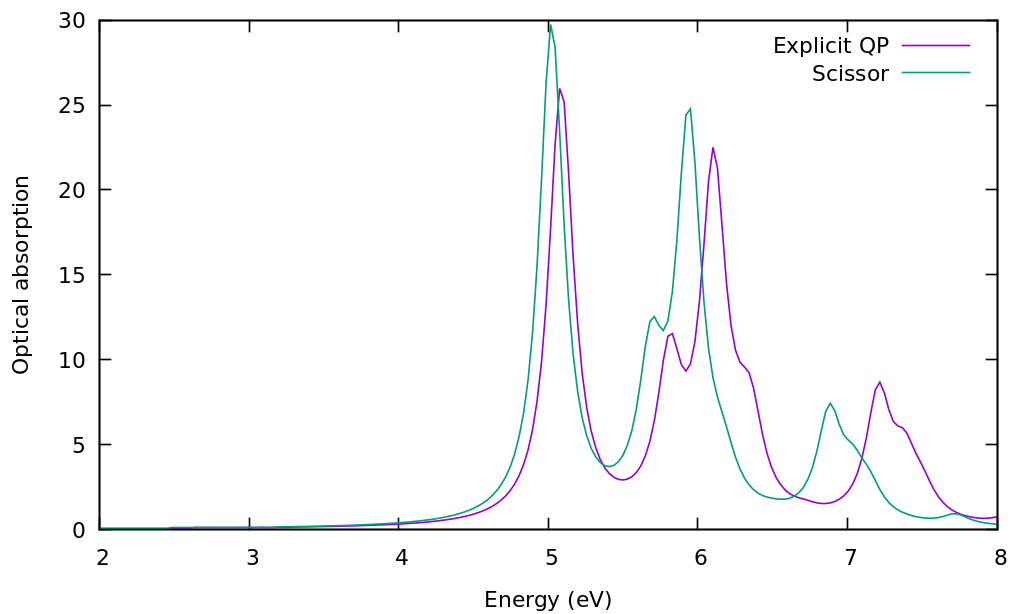
plot 'o-3D_QP_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse' u 1:2 w l t 'Explicit QP', 'o-3D_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse' u 1:2 w l t 'Scissor' | plot 'o-3D_QP_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse' u 1:2 w l t 'Explicit QP', 'o-3D_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse' u 1:2 w l t 'Scissor' | ||
[[File:03 bse diago qp.png|none|600px]] | [[File:03 bse diago qp 2021.png|none|600px]] | ||
It is clear that this makes a difference in the peak distribution and intensity. Note that | |||
It is clear that this makes a difference in the peak positions, distribution and intensity. Note that besides a simple shift you can renormalise as well the bandwidth of the valence and conduction bands in <code>KfnQP_E</code> (respectively the third and second value). You can try as an exercise to set up a new calculation using e.g. <code> 1.44 | 1.200000 | 0.900000 |</code> for <code>KfnQP_E</code>. | |||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| Line 34: | Line 49: | ||
* How to compute the optical spectrum including quasiparticle corrections (full GW+BSE calculation). | * How to compute the optical spectrum including quasiparticle corrections (full GW+BSE calculation). | ||
== | ==Navigate== | ||
* Previous module: [[Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization]] | * Previous module: [[Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization]] | ||
* Back to [[Calculating optical spectra including excitonic effects: a step-by-step guide]] tutorial | * Back to [[Calculating optical spectra including excitonic effects: a step-by-step guide]] tutorial | ||
* Back to [[Rome 2023#Tutorials]] | |||
* [[Tutorials|Back to tutorials menu]] | * [[Tutorials|Back to tutorials menu]] | ||
* [[Modules|Back to technical modules menu]] | * [[Modules|Back to technical modules menu]] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:30, 5 December 2024
In this module, you will learn how to include GW-corrected (QP) energies in the calculation of the absorption spectrum. The energy differences on the diagonal of the excitonic Hamiltonian are added before the solution of the Bethe-Salpeter eigenproblem, therefore only that step needs to be repeated if we change the QP corrections.
Prerequisites
Previous modules You must have completed
- the BSE kernel tutorial
- the Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization tutorial, in which a simple scissor operator is used for the QP corrections.
You will need:
- The
SAVEdatabases for 3D hBN - The
3D_BSEdirectory containing the databases from the Static screening, Bethe-Salpeter kernel, Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization modules thus containing thendb.BS_Q1_CPU_0andndb.em1s*databases for 3D hBN - The
GW_QP_databasedirectory (provided) which contains the database with the GW corrections (you can also use the ndb.QP file produced in the GW tutorial) yamboexecutable
Reading the QP corrections from a previous GW calculation
In the previous step we used a simple scissor operator to correct the Kohn-Sham DFT energies. Instead, in this part, we are taking the QP corrections from a previous Yambo GW calculation.
We create and edit the input:
$ yambo -F 03_3D_QP_BSE.in -y d -V qp -J 3D_BSE
We set all parameters as in the previous step, except for the part regarding the QP correction:
KfnQPdb= "E < GW_QP_database/ndb.QP" # [EXTQP BSK BSS] Database KfnQP_INTERP_NN= 1 # [EXTQP BSK BSS] Interpolation neighbours % KfnQP_E 0.000000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | # [EXTQP BSK BSS] E parameters (c/v) eV|adim|adim %
Instead of setting the values for the scissor, we give the path to the database that contains the QP corrections (GW_QP_database/ndb.QP). The latter was created by running a GW calculation as in Step 3 of the GW tutorial. For more info about how the QP corrections are loaded you can also check this page: Loading QP corrections.
Run Yambo:
$ yambo -F 03_3D_QP_BSE.in -J "3D_QP_BSE,3D_BSE"
Note how we specified multiple directories, separated by a comma. This instructs Yambo to look for databases that may be already present from previous steps of the calculations in all the listed folders. If you completed the previous section of the tutorial, then you should have the 3D_BSE folder with ndb.dipoles_*, ndb.em1s* and ndb.BS_CPU* databases, which will not be recalculated by Yambo: the code will repeat only the diagonalization step - also reading the QP database - and print the resulting databases in the new folder 3D_QP_BSE. If you don't have the 3D_BSE folder, you have to repeat the entire BSE calculation, therefore you just need to give the option "-J 3D_QP_BSE,GW_QP_database".
This produces the following log in the standard output. Note Section 4 (regarding external QP corrections to the kernel):
<---> [04] External/Internal QP corrections <---> E<GW_QP_database/ndb.QP[ PPA@E 27.21138 = XG 5 = Xb 1-40 = Scb 1-40] <---> [dE_from_DB-Nearest K] Exact matches : 100.0000 [o/o]
This tells you that the file was found, read correctly and that the k points found in the file matched the ones you are using for the current calculation (otherwise interpolation would be needed). It is crucial to check that the file has been read, since if not Yambo gives a warning but continues the calculation (with no QP corrections at all!). As in the calculation with the scissor shift the final results are the files with the macroscopic dielectric functions. Let's compare the results for the optical absorption spectrum with those obtained previously with a simple scissor:
$ gnuplot ... plot 'o-3D_QP_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse' u 1:2 w l t 'Explicit QP', 'o-3D_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse' u 1:2 w l t 'Scissor'
It is clear that this makes a difference in the peak positions, distribution and intensity. Note that besides a simple shift you can renormalise as well the bandwidth of the valence and conduction bands in KfnQP_E (respectively the third and second value). You can try as an exercise to set up a new calculation using e.g. 1.44 | 1.200000 | 0.900000 | for KfnQP_E.
Summary
From this tutorial you've learned:
- How to compute the optical spectrum including quasiparticle corrections (full GW+BSE calculation).