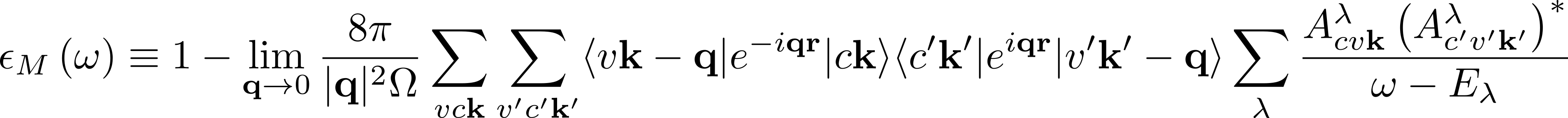Bethe-Salpeter solver: diagonalization: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
In this module you learn how to obtain an optical absorption | In this module, you learn how to obtain an optical absorption spectrum within the Bethe-Salpeter equation (BSE) framework by diagonalizing a previously calculated Bethe-Salpeter (BS) kernel. | ||
==Prerequisites== | ==Prerequisites== | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
[[File:BSE1-Eq4.png|none|x50px]] | [[File:BSE1-Eq4.png|none|x50px]] | ||
To get the two-particle Hamiltonian eigensolutions you need to diagonalize the two-particle Hamiltonian (non spin-polarized case): | To get the two-particle Hamiltonian eigensolutions you need to diagonalize the two-particle Hamiltonian (non-spin-polarized case): | ||
[[File:BSE1-Eq1.png|none|x50px]] | [[File:BSE1-Eq1.png|none|x50px]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
The difference of quasiparticle energies ''Δε<sub>cv'''k'''</sub>= ε<sub>c'''k'''</sub> - ε<sub>v'''k'''</sub>'' is added to the matrix just before the solver. | The difference of quasiparticle energies ''Δε<sub>cv'''k'''</sub>= ε<sub>c'''k'''</sub> - ε<sub>v'''k'''</sub>'' is added to the matrix just before the solver. | ||
There are two possible choices: | There are two possible choices: | ||
* the Kohn-Sham energies (calculated at DFT level) are corrected through a | * the Kohn-Sham energies (calculated at DFT level) are corrected through a scissor and the renormalization of the conduction and valence bandwidth (linearly for the conduction band minimum and the valence band maximum respectively): | ||
''Δε<sub>cv'''k'''</sub>= M<sub>c</sub>(ε<sub>c'''k'''</sub><sup>KS</sup> - CBM) - M<sub>v</sub>(ε<sub>v'''k'''</sub><sup>KS</sup> - VBM) + Scissor'' | ''Δε<sub>cv'''k'''</sub>= M<sub>c</sub>(ε<sub>c'''k'''</sub><sup>KS</sup> - CBM) - M<sub>v</sub>(ε<sub>v'''k'''</sub><sup>KS</sup> - VBM) + Scissor'' | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
1.440000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | | 1.440000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | | ||
% | % | ||
This gives the quasiparticle corrections to the Kohn-Sham eigenvalues and | This gives the quasiparticle corrections to the Kohn-Sham eigenvalues and is deduced either from experiment or previous [[How to obtain the quasi-particle band structure of a bulk material: h-BN|GW calculations]]. | ||
With reference to the equation in the Background, the format is | With reference to the equation in the Background, the format is | ||
''Scissor'' | ''M<sub>c</sub>'' | ''M<sub>v</sub>'' | | ''Scissor'' | ''M<sub>c</sub>'' | ''M<sub>v</sub>'' | | ||
The alternative of directly input corrections calculated from a previous GW calculation is shown in the [[Bethe-Salpeter on top of quasiparticle energies|next section]]. | The alternative of directly input corrections calculated from a previous GW calculation is shown in the [[Bethe-Salpeter on top of quasiparticle energies|next section]]. | ||
'''Important''': | '''Important''': to analyse the exciton composition and plot the exciton wave function in the [[How to analyse excitons - CECAM 2021 school|postprocessing tutorial]], you must uncomment the following flag: | ||
WRbsWF # [BSS] Write to disk excitonic the WFs | WRbsWF # [BSS] Write to disk excitonic the WFs | ||
This writes the eigenvectors | |||
==Bethe-Salpeter solver runlevel== | ==Bethe-Salpeter solver runlevel== | ||
| Line 86: | Line 88: | ||
Take some time to inspect the log and the report to check the consistency with the input variables. This run produces a new database in the 3D_BSE directory | Take some time to inspect the log and the report to check the consistency with the input variables. This run produces a new database in the 3D_BSE directory | ||
3D_BSE/ndb.BS_diago_Q01 | 3D_BSE/ndb.BS_diago_Q01 | ||
So if you need the spectrum on a different energy range, direction, with a different broadening or | So if you need the spectrum on a different energy range, direction, with a different broadening or more points the diagonalization is not repeated, just the spectrum is recalculated. | ||
Note that this database, as well as any other netCDF-format database produced by | Note that this database, as well as any other netCDF-format database produced by Yambo, can be directly accessed and read using [[First steps in Yambopy| python modules]]. | ||
This run produces as well human readable files (o-*). Specifically <code>o-3D_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse</code> contains the real and imaginary part of the macroscopic dielectric function | This run produces as well human readable files (o-*). Specifically <code>o-3D_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse</code> contains the real and imaginary part of the macroscopic dielectric function | ||
| Line 103: | Line 105: | ||
Energy in eV | Imaginary part BSE | Real part BSE |Imaginary part IPA | Real part IPA | | Energy in eV | Imaginary part BSE | Real part BSE |Imaginary part IPA | Real part IPA | | ||
where real and imaginary parts refer to the macroscopic dielectric function. The imaginary part is related to | where real and imaginary parts refer to the macroscopic dielectric function. The imaginary part is related to optical absorption. The latter (column 2) can be plotted versus the photon energy (column 1) and compared with the independent particle approximation (IPA, column 4), e.g.: | ||
$ gnuplot | $ gnuplot | ||
| Line 110: | Line 112: | ||
[[file:03_bse_diago.png |none|600px]] | [[file:03_bse_diago.png |none|600px]] | ||
The addition of the kernel has the effect to red-shift the spectrum onset and | The addition of the kernel has the effect to red-shift the spectrum onset and redistribute the oscillator strengths. Note that the convergence for k-points smooths out the low energy peaks in the IPA (which are an artefact of poor convergence with k-points producing artificial confinement) to give the shoulder corresponding to the van Hove singularity in the band structure. On the other hand, the low energy peak in the BSE is genuine and it is the signature of a bound exciton. | ||
==Summary== | ==Summary== | ||
| Line 116: | Line 118: | ||
* How to compute the optical spectrum by using the diagonal solver within the Bethe-Salpeter equation framework | * How to compute the optical spectrum by using the diagonal solver within the Bethe-Salpeter equation framework | ||
== | ==Navigate== | ||
* Previous module: [[Bethe-Salpeter kernel]] | * Previous module: [[Bethe-Salpeter kernel]] | ||
Revision as of 17:01, 28 March 2021
In this module, you learn how to obtain an optical absorption spectrum within the Bethe-Salpeter equation (BSE) framework by diagonalizing a previously calculated Bethe-Salpeter (BS) kernel.
Prerequisites
- You must first complete the Static screening and Bethe-Salpeter kernel modules
You will need:
- The
SAVEdatabases for 3D hBN - The
3D_QP_BSEdirectory (provided) which contains the database with the GW corrections (create one directory with this name and put the ndb.QP file produced yesterday there) - The
3D_BSEdirectory containing the databases from the Static screening and Bethe-Salpeter kernel modules - The
yamboexecutable gnuplotfor plotting spectra
Background
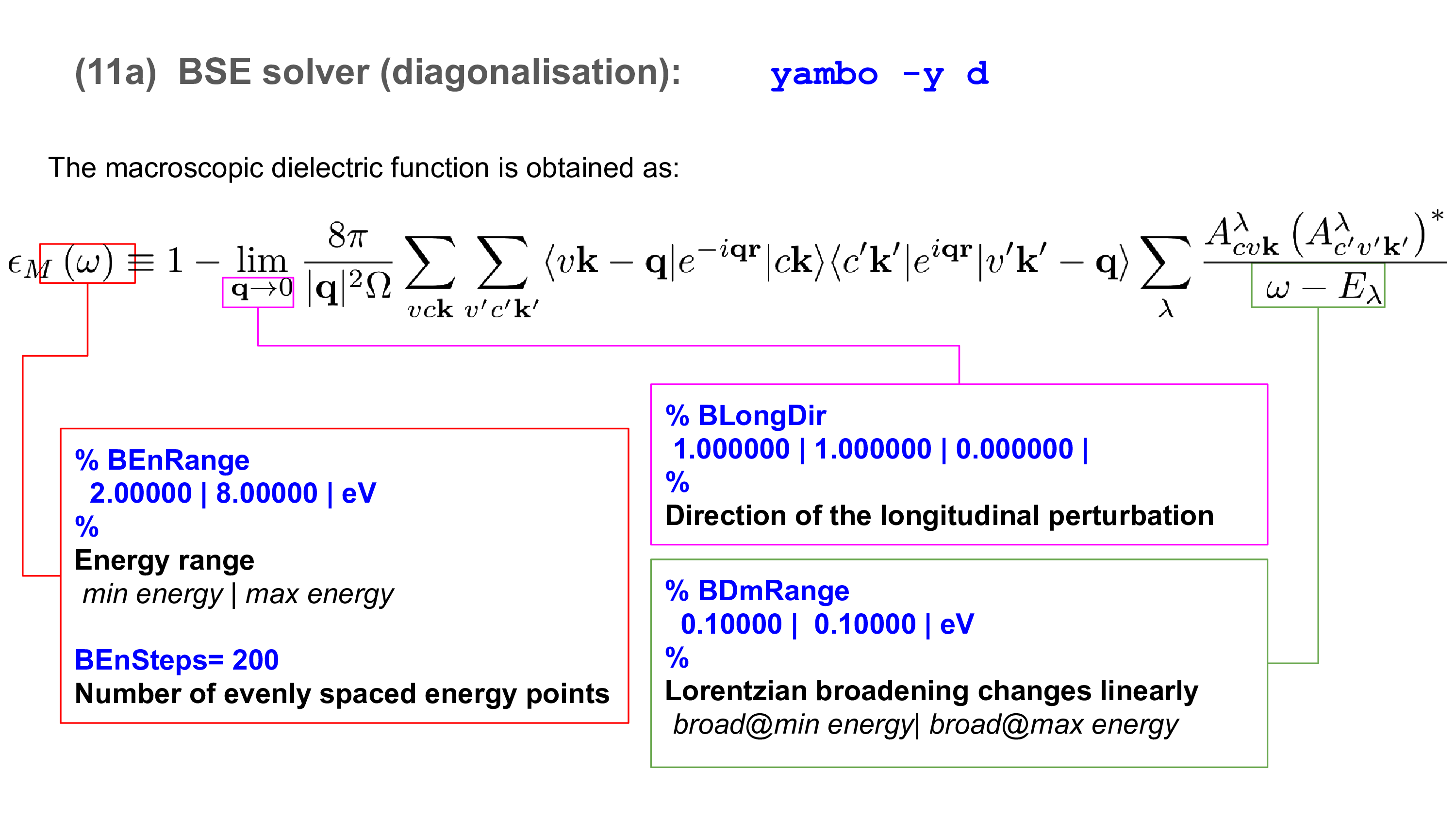
The macroscopic dielectric function (from which the absorption and EEL spectra can be computed) is obtained from the eigenvalues Eλ (excitonic energies) and eigenvectors Aλcvk (exciton composition in terms of electron-hole pairs) of the two-particle Hamiltonian:
To get the two-particle Hamiltonian eigensolutions you need to diagonalize the two-particle Hamiltonian (non-spin-polarized case):
for which the 2V - W part was evaluated in the Bethe-Salpeter kernel module.
The difference of quasiparticle energies Δεcvk= εck - εvk is added to the matrix just before the solver. There are two possible choices:
- the Kohn-Sham energies (calculated at DFT level) are corrected through a scissor and the renormalization of the conduction and valence bandwidth (linearly for the conduction band minimum and the valence band maximum respectively):
Δεcvk= Mc(εckKS - CBM) - Mv(εvkKS - VBM) + Scissor
- the quasiparticle energies calculated at GW level are used (see next tutorial. Missing energies are computed by interpolation.
Choosing the input parameters
Invoke yambo with the "-y d" option in the command line:
$ yambo -F 03_3D_BSE_diago_solver.in -y d -V qp -J 3D_BSE
The input is open in the editor. The input variable to be changed are
% BEnRange 2.00000 | 8.00000 | eV % BEnSteps= 200
which define 200 evenly spaced points between 2 and 8 eV at which the spectrum is calculated (ω in the equation for the macroscopic dielectric function),
% BDmRange 0.10000 | 0.10000 | eV %
which defines the spectral broadening (Lorentzian model),
% BLongDir 1.000000 | 1.000000 | 0.000000 | %
which defines the direction of the perturbing electric field (in this case the in-plane direction).
Another parameter to modify is
% KfnQP_E 1.440000 | 1.000000 | 1.000000 | %
This gives the quasiparticle corrections to the Kohn-Sham eigenvalues and is deduced either from experiment or previous GW calculations. With reference to the equation in the Background, the format is
Scissor | Mc | Mv |
The alternative of directly input corrections calculated from a previous GW calculation is shown in the next section.
Important: to analyse the exciton composition and plot the exciton wave function in the postprocessing tutorial, you must uncomment the following flag:
WRbsWF # [BSS] Write to disk excitonic the WFs
This writes the eigenvectors
Bethe-Salpeter solver runlevel
$ yambo -F 03_3D_BSE_diago_solver.in -J 3D_BSE
In the log (either in standard output or in l-3D_BSE_optics_dipoles_bss_bse), after various setup/loading, the BSE is diagonalized using the linked linear algebra libraries:
<---> [03] BSE solver(s) @q1 <---> [LA] SERIAL linear algebra <---> [03.01] Diago Solver @q1 <---> BSK diagonalize |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X) <---> EPS R residuals |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X) <---> BSK resp. funct |########################################| [100%] --(E) --(X)
The report r-3D_BSE_optics_dipoles_bss_bse contains information relative to this runlevel in section 3:
[03] BSE solver(s) @q1 ======================
Take some time to inspect the log and the report to check the consistency with the input variables. This run produces a new database in the 3D_BSE directory
3D_BSE/ndb.BS_diago_Q01
So if you need the spectrum on a different energy range, direction, with a different broadening or more points the diagonalization is not repeated, just the spectrum is recalculated. Note that this database, as well as any other netCDF-format database produced by Yambo, can be directly accessed and read using python modules.
This run produces as well human readable files (o-*). Specifically o-3D_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse contains the real and imaginary part of the macroscopic dielectric function
$ less o-3D_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse ... # # E/ev[1] EPS-Im[2] EPS-Re[3] EPSo-Im[4] EPSo-Re[5] # 2.00000 0.16162 5.83681 0.04959 4.14127 2.03015 0.16787 5.88612 0.05090 4.15638 ...
which is in the format
Energy in eV | Imaginary part BSE | Real part BSE |Imaginary part IPA | Real part IPA |
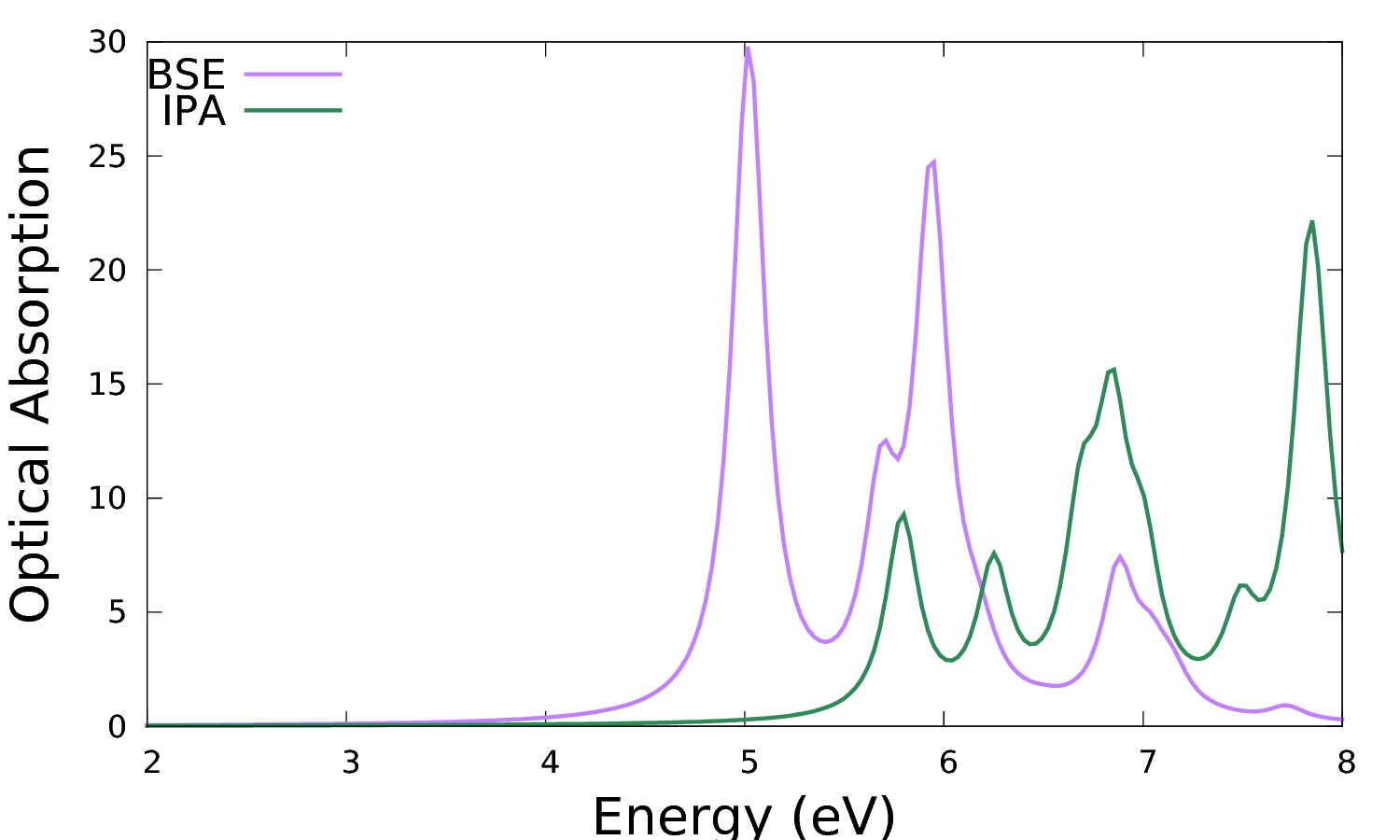
where real and imaginary parts refer to the macroscopic dielectric function. The imaginary part is related to optical absorption. The latter (column 2) can be plotted versus the photon energy (column 1) and compared with the independent particle approximation (IPA, column 4), e.g.:
$ gnuplot ... plot 'o-3D_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse' u 1:2 w l t 'BSE', 'o-3D_BSE.eps_q1_diago_bse' u 1:4 w l t 'IPA'
The addition of the kernel has the effect to red-shift the spectrum onset and redistribute the oscillator strengths. Note that the convergence for k-points smooths out the low energy peaks in the IPA (which are an artefact of poor convergence with k-points producing artificial confinement) to give the shoulder corresponding to the van Hove singularity in the band structure. On the other hand, the low energy peak in the BSE is genuine and it is the signature of a bound exciton.
Summary
From this tutorial you've learned:
- How to compute the optical spectrum by using the diagonal solver within the Bethe-Salpeter equation framework
- Previous module: Bethe-Salpeter kernel
- Next module: Bethe-Salpeter on top of quasiparticle energies
- Alternative Bethe-Salpeter equation solver: Lanczos-Haydock
- Alternative Bethe-Salpeter equation solver: Slepc
- Exciton analysis: How to analyse excitons - CECAM 2021 school
- Back to Calculating optical spectra including excitonic effects: a step-by-step guide tutorial
- Back to tutorials menu
- Back to technical modules menu